📌 What It Is
Story Breakdown: mmNorm Technology by MIT
- mmNorm is a novel imaging system developed by researchers at MIT.
- It uses millimeter wave (mmWave) signals (similar to Wi-Fi) to reconstruct detailed 3D shapes of objects hidden from view.
- The key innovation? It doesn’t just collect signal reflections—it calculates the “surface normals” (the direction a point on a surface is facing), leading to vastly improved reconstruction accuracy.
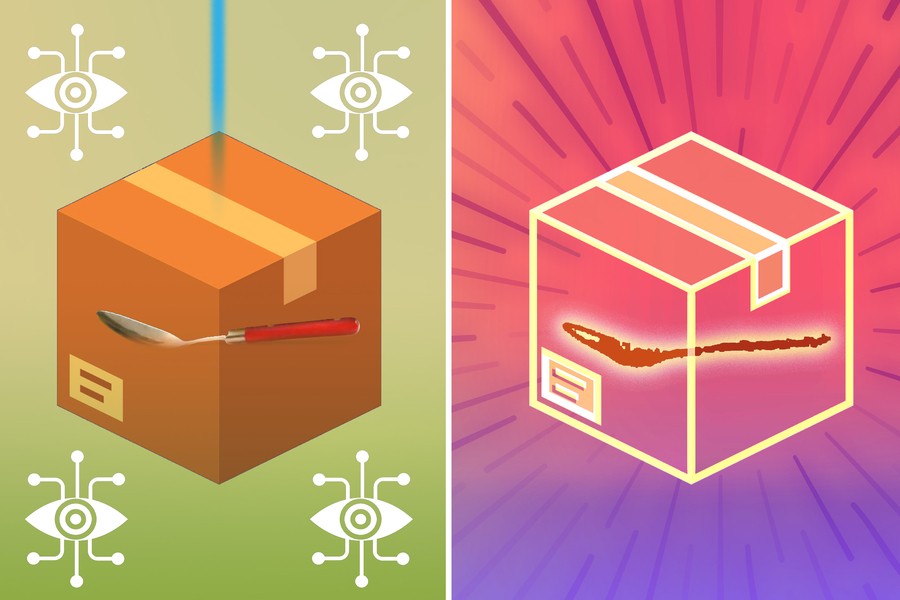
🧪 How It Works
- A radar-equipped robot arm sends mmWave signals that penetrate materials like plastic or cardboard.
- Reflections from the object’s surface are received by multiple antennas.
- Each antenna votes on the orientation of the surface based on the signal’s strength.
- These estimations combine into a coherent, detailed 3D model.
📊 Results & Advantages
- 96% accuracy in reconstructing objects—compared to 78% from traditional methods.
- Excels with complex shapes (e.g., mugs, power tools) and various materials (metal, rubber, glass).
- Can distinguish between multiple occluded objects like different utensils in a box.

🛠️ Proposed Uses
- Warehousing: Quality control robots detect defects inside sealed packages.
- Elder Care & Factories: Home robots grasp obscured tools or objects safely.
- AR/VR: See-through overlays for industry applications.
- Security: Screening luggage or enclosed spaces at airports.
- Military Recon: Surveillance or intel gathering behind obstructions

⚖️ The Big Question: Privacy and Ethical Boundaries
While the science is breathtaking, it also raises serious concerns. Here are the critical angles to consider:
👁️ Surveillance Overreach
- Devices with this tech could see through walls, boxes, or vehicles, potentially without the subject’s knowledge or consent.
- Could enable warrantless scanning in homes, vehicles, or private property—raising Fourth Amendment questions in the U.S. (which protects against unreasonable search and seizure).
🕵️ Potential for Misuse
- Authoritarian governments or corrupt officials might deploy it to spy on dissidents.
- Private actors (landlords, employers, stalkers) might exploit similar tools for covert monitoring or surveillance.
- Companies could use it to “see into” competitors’ operations or consumer behavior in unethical ways.
🧩 Legal & Ethical Grey Areas
- Unlike visual cameras, mmWave tech operates silently and invisibly—harder for people to detect or opt out of.
- Even if legally permitted in public spaces, covert use blurs the line between reasonable oversight and invasive surveillance.
- The lack of established legal frameworks for such signal-based imaging systems makes them ripe for abuse if left unchecked.
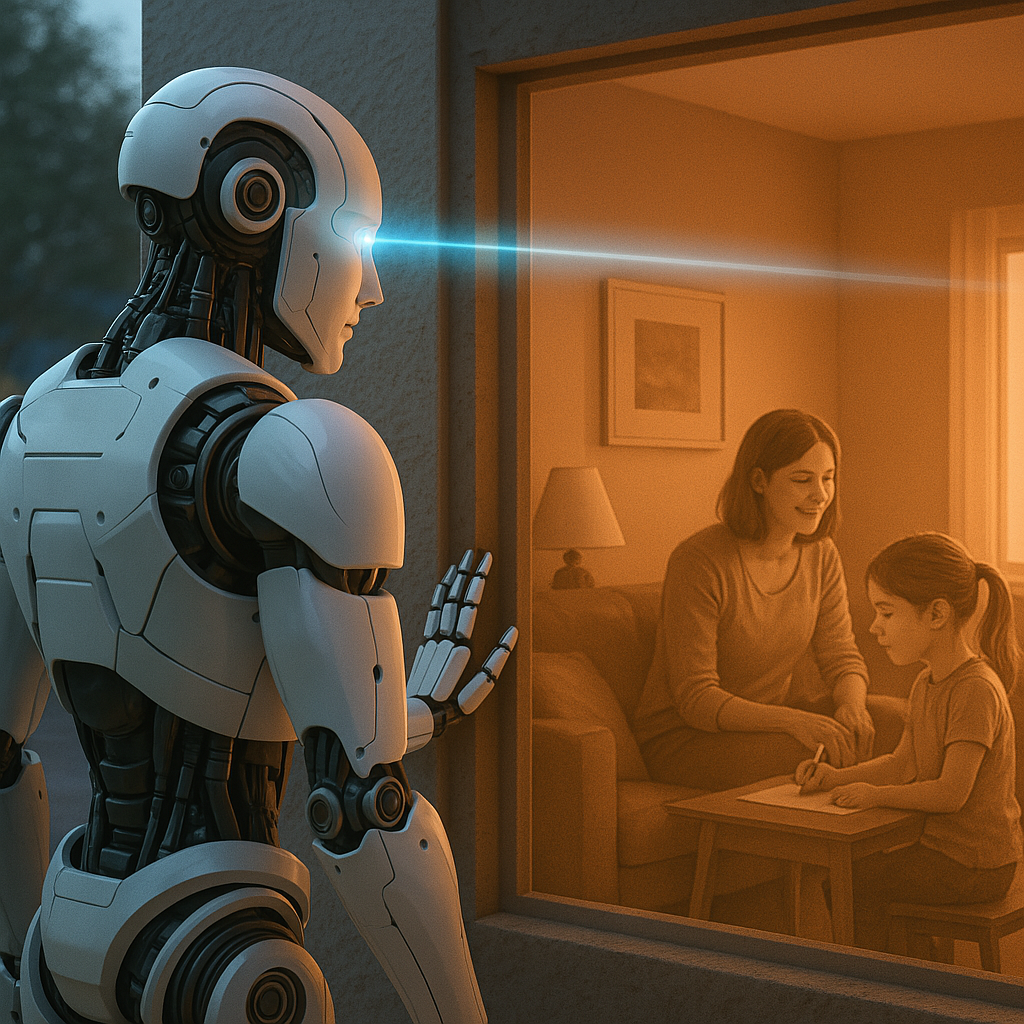
🧭 Path Forward: Innovation with Safeguards
To prevent misuse while enabling progress, society might need to:
- 🔒 Define explicit legal limits for non-consensual deployment of mmWave scanners.
- 🧑⚖️ Require warrants or legal oversight before using it for surveillance or search.
- 🧠 Build privacy safeguards and logging into hardware/software to detect and audit use.
- 🔬 Encourage open standards and transparency in development to ensure accountability.
🥜 The Final Nut
This tech could transform sectors from logistics to rescue ops—but it also redefines what it means to be “seen.” The question is: Will the law and ethics catch up before the machines do? Read the Full Report Here: MIT News
Comment your thoughts below, or Contact Us with your concerns


Leave a Reply